Sprint 3 Learning Blog
Personal blog about things I learned from the lessons in Sprint 3
Building a Python API and a Javascript Frontend
Python API
APIs are used to create a way for other programs to interact with your program. They allow you to create a bridge between your program and other programs.
In our case, we used a Python API to converse between our flask server and our Javascript frontend.
Database
We used a cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) policy to allow our Javascript frontend to access our flask server. The database contains tables and columns that are accessed by our Python API. On the frontend, we used the Fetch API to send a request to our Python API. The Python API then sends a response back to the frontend, and we display the data.
No SQL vs MySQL Databases
MySQL and NoSQL databases are two different approaches to storing and managing data. MySQL databases are relational, meaning they use tables to organize data in rows and columns with fixed schemas, making them good for applications that require structured data and complex queries. They use Structured Query Language (SQL) for defining and manipulating data, which is standardized and consistent across systems.
On the other hand, NoSQL databases are non-relational and more flexible with their data models. They can store unstructured or semi-structured data, allowing for formats like key-value pairs, documents, graphs, or wide-column stores. This flexibility makes them better for handling large volumes of varied data and scaling horizontally. NoSQL databases are often used for big data and real-time web applications, with examples like MongoDB, Cassandra, and Redis. In summary, SQL databases are structured, reliable, and standardized, while NoSQL databases offer flexibility and scalability for diverse, fast-changing data.
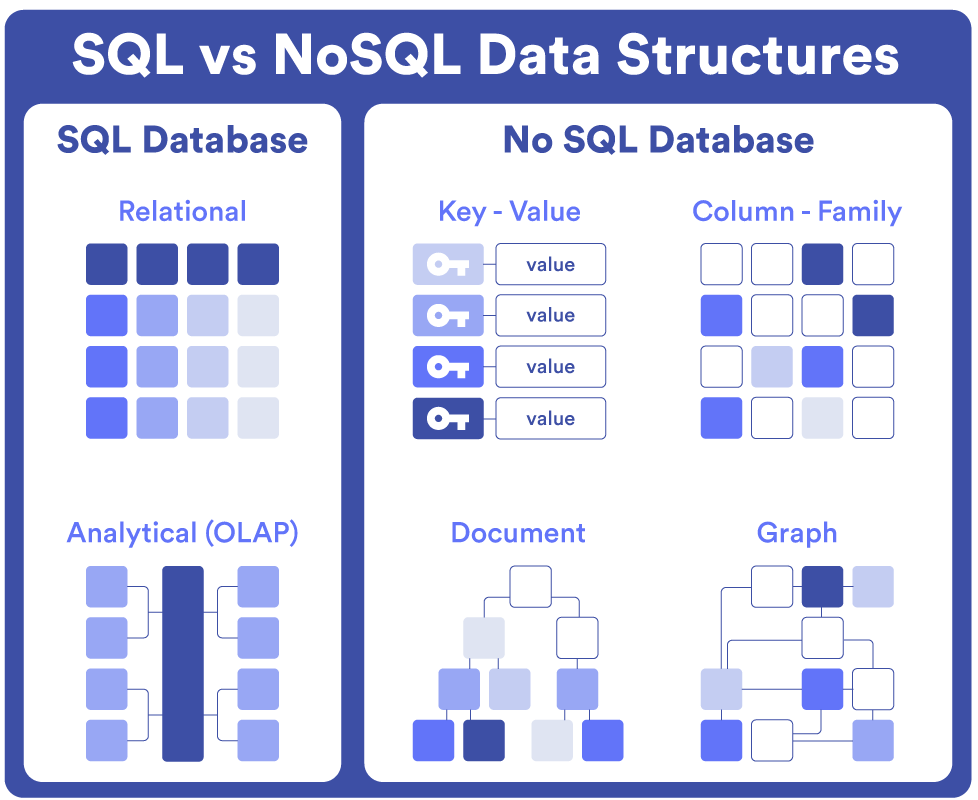
In short, MySQL databases are more structured and have relational tables such as the user_id we have in the carChat table.
Applying this to our situation
We chose to store our car data within the user table as a column. This mimics the same idea of a NoSql database because the only way to access a car is through a user. So if you want to fetch a table of all the cars you would have to go through each user. If we chose to make a table dedicated to cars and give each car a UserId (create a relationship between the car and user), we could fetch all the cars and fetch a car from a user.
Looking Back
Looking back, I think that for our garage to function a lot smoother with our myCar page, we should have dedicated a table to storing data for cars. This would be the most optimal way to store data for this use.
Chat System
In our database, my group has a table called carChats which has the columns: id, message, and user_id.
- The id column is generated by SQLAlchemy’s autoincrementer.
- The message column is a string found in the body of the request
- The user_id column is an id that links the chat to the user who sent it.